ERA-RARE-Cofund-Improve CPVT
Contract Nr 19/2016 UEFSCDI
Improving the diagnosis and treatment of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia: integrating clinical and basic science
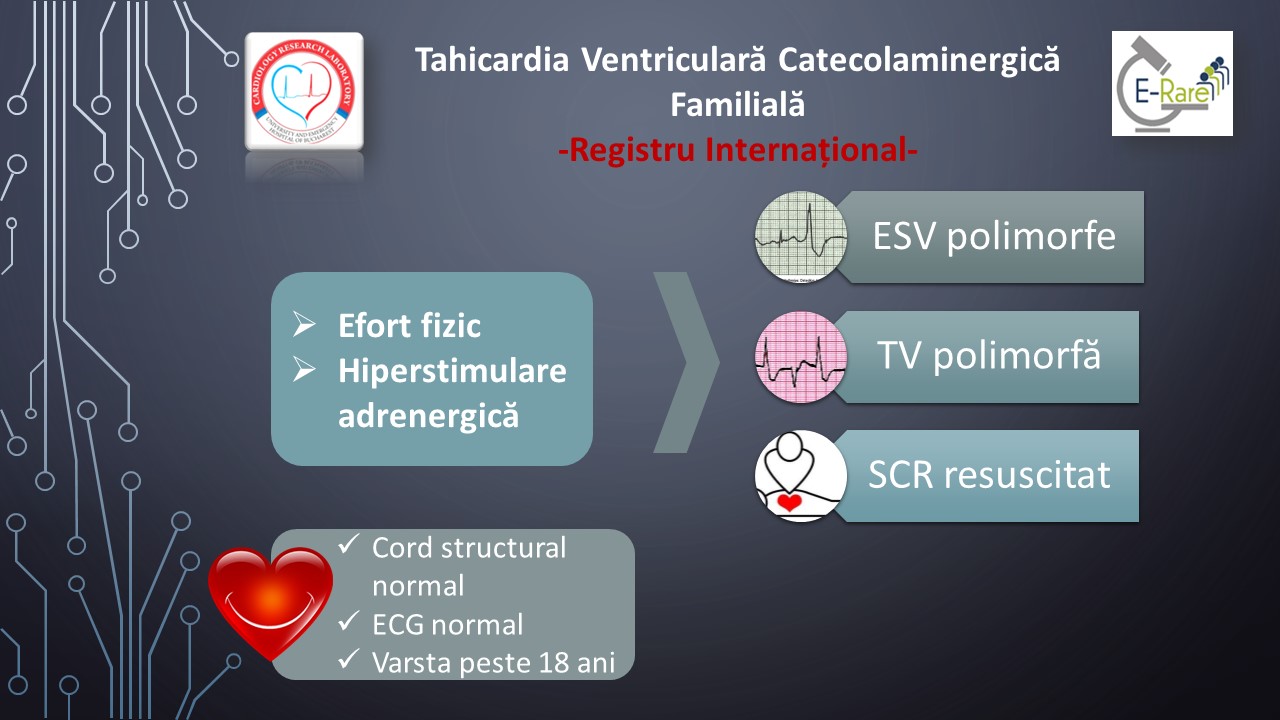
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is an inherited cardiac arrhythmia syndrome with a prevalence of 1/10 000 that causes sudden cardiac death (SCD). It is one of the most lethal pathologies involving ion channels and is most commonly due to mutations in the ryanodine receptor 2 (RYR2).
The diagnosis of CPVT is challenging because the patients present with exercise- or emotion-induced ventricular arrhythmias without abnormalities in resting ECG or cardiac structure. At present, neither optimal risk stratification tools, nor effective interventions for CPVT are available to the treating cardiologists.
This project brings together global clinical leaders and basic scientists with expertise in inherited arrhythmia conditions and national and international registries. The overall purpose of this research program is to develop an effective strategy for rationalizing therapies based on an individuals’ risk profile, thereby reducing morbidity and preventing SCD. We will establish an international CPVT registry and a corresponding biobank to enable identification of relevant new genes, to correlate genotype with phenotype, and to generate risk prediction algorithms for clinical use. Further, we will enhance our understanding of RYR2 mutations in CPVT by performing basic research.
By treating CPVT patients according to risk stratification based on demographics, family history, clinical presentation, genetics, and functional characteristics, we aim to improve patient outcomes and save lives.
Results and activities, first period (July-December 2016)
Results and activities, second period (December 2016-December 2017)
Results and activities, third period (December 2017-December 2018)
Results and activities, third period (December 2018-June 2019)